Unit 10 homework 5 inscribed angles – Unit 10 Homework 5: Inscribed Angles and Their Applications delves into the fascinating realm of geometry, where we explore the intricate relationship between inscribed angles and intercepted arcs. This exploration unveils a treasure trove of knowledge, offering valuable insights into the measurement, types, properties, and practical applications of inscribed angles.
Inscribed angles, nestled within the confines of geometric figures, possess unique characteristics that distinguish them from their counterparts. Their intimate connection with intercepted arcs provides a foundation for understanding the behavior of angles formed within circles and other curved shapes.
Inscribed Angles and Intercepted Arcs
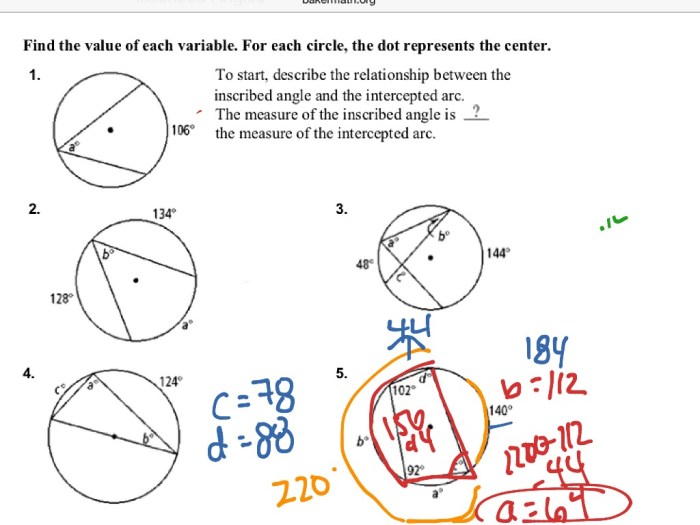
In geometry, an inscribed angle is an angle whose vertex lies on a circle and whose sides intersect the circle. The intercepted arc is the portion of the circle that lies between the sides of the inscribed angle.
The measure of an inscribed angle is half the measure of its intercepted arc. This relationship is known as the Inscribed Angle Theorem.
Examples
- In a circle, an inscribed angle that intercepts a semicircle is a right angle.
- In a circle, an inscribed angle that intercepts a quarter circle is a 45-degree angle.
- In a circle, an inscribed angle that intercepts a third of a circle is a 60-degree angle.
Measuring Inscribed Angles: Unit 10 Homework 5 Inscribed Angles
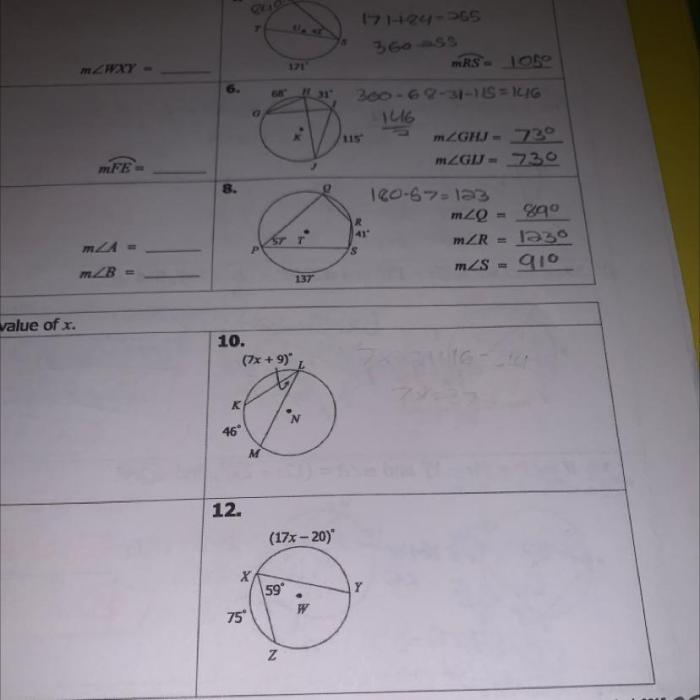
Inscribed angles are angles that are formed when two chords intersect inside a circle. Measuring inscribed angles is important because it allows us to determine the measure of the arc that is intercepted by the angle.
To measure an inscribed angle, we can use the following steps:
Steps for Measuring Inscribed Angles
- Draw the circle and the inscribed angle.
- Label the center of the circle as O.
- Label the points of intersection of the chords as A and B.
- Draw the radii OA and OB.
- Measure the angle ∠AOB. This is the measure of the inscribed angle.
Types of Inscribed Angles
Inscribed angles are classified into three types based on their position relative to the circle and the intercepted arc:
1. Central Inscribed Angle:
- Formed by two radii of the circle.
- Vertex lies at the center of the circle.
- Intercepts an arc that is half the circumference of the circle.
2. Inscribed Angle:
- Formed by two chords of the circle.
- Vertex lies on the circle.
- Intercepts an arc that is less than half the circumference of the circle.
3. Semi-Inscribed Angle:
- Formed by a radius and a chord of the circle.
- Vertex lies on the circle.
- Intercepts an arc that is greater than half the circumference of the circle.
Properties of Inscribed Angles
Inscribed angles are those formed by two chords intersecting inside a circle. They have specific properties that are useful in solving geometry problems.
Properties of Inscribed Angles
- The measure of an inscribed angle is half the measure of its intercepted arc.
- Inscribed angles that intercept the same arc are congruent.
- An angle inscribed in a semicircle is a right angle.
- The sum of the measures of two inscribed angles that intercept adjacent arcs is 180 degrees.
Applications of Properties of Inscribed Angles, Unit 10 homework 5 inscribed angles
These properties can be used to solve a variety of geometry problems, such as:
- Finding the measure of an inscribed angle
- Finding the measure of an intercepted arc
- Determining whether two inscribed angles are congruent
- Solving problems involving angles inscribed in semicircles
Applications of Inscribed Angles
Inscribed angles have practical applications in various fields, including architecture, design, and engineering. Understanding the properties and measurements of inscribed angles enables professionals to design and construct structures with precision and aesthetic appeal.
Architecture
In architecture, inscribed angles are used to create aesthetically pleasing and structurally sound designs. For instance, architects may use inscribed angles to design arched doorways or windows, ensuring symmetry and balance in the overall structure. Additionally, inscribed angles can be employed to calculate the optimal placement of support beams and columns, ensuring the stability and longevity of the building.
Design
In the field of design, inscribed angles are utilized to create visually appealing and functional objects. For example, graphic designers may use inscribed angles to design logos or patterns that are symmetrical and harmonious. Similarly, interior designers may use inscribed angles to determine the optimal placement of furniture and décor, creating a visually pleasing and cohesive space.
Engineering
In engineering, inscribed angles play a crucial role in designing and constructing bridges, tunnels, and other infrastructure projects. Engineers use inscribed angles to calculate the angles of support beams, trusses, and arches, ensuring the structural integrity and stability of these structures.
Additionally, inscribed angles are used in the design of gears and pulleys, ensuring smooth and efficient operation of machinery.
Key Questions Answered
What is an inscribed angle?
An inscribed angle is an angle whose vertex lies on a circle and whose sides intersect the circle.
How do you measure an inscribed angle?
To measure an inscribed angle, find the measure of its intercepted arc and divide it by 2.
What are the different types of inscribed angles?
There are three types of inscribed angles: acute, right, and obtuse.
What are the properties of inscribed angles?
Inscribed angles have several properties, including the inscribed angle theorem, which states that the measure of an inscribed angle is half the measure of its intercepted arc.
What are some applications of inscribed angles?
Inscribed angles are used in a variety of applications, including architecture, design, and engineering.