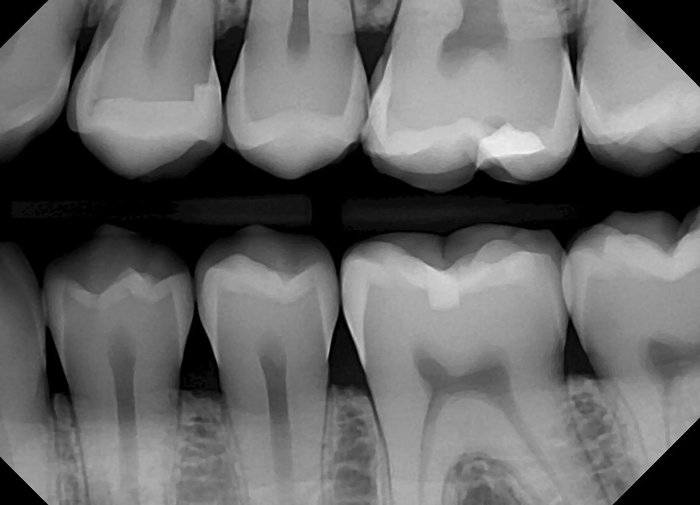
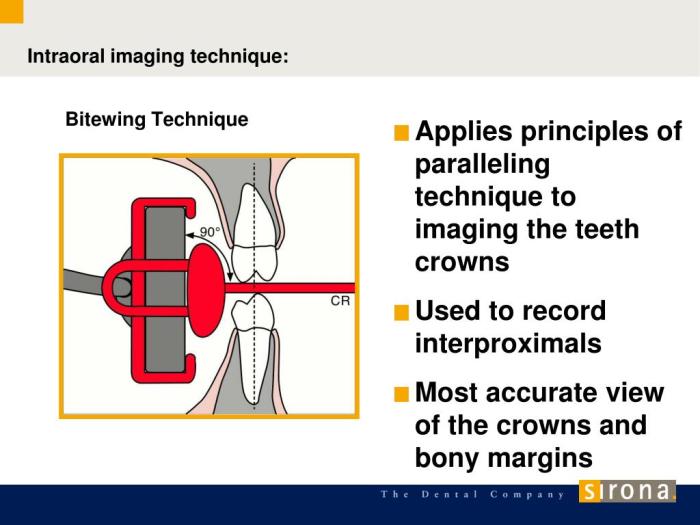
Basic principles of the bitewing technique include the: – The bitewing technique is a fundamental aspect of dental radiography, providing crucial diagnostic information for caries detection and interproximal assessment. This guide will delve into the basic principles of the bitewing technique, encompassing horizontal and vertical angulation, tube position and distance, patient positioning, film placement, exposure parameters, and image evaluation.
Basic Principles of the Bitewing Technique
Bitewing radiography is an essential diagnostic tool in dentistry, providing valuable information about the interproximal surfaces of the teeth. To obtain optimal images, it is crucial to adhere to the basic principles of the technique, including proper horizontal and vertical angulation, tube position and distance, patient positioning, film placement, exposure parameters, and image evaluation.
Horizontal Angulation
Horizontal angulation refers to the angle at which the X-ray beam is directed towards the teeth. Correct horizontal angulation is essential for capturing clear and undistorted images of the interproximal surfaces. If the angulation is too steep, the beam will pass over the contact points, resulting in inadequate visualization of the interproximal areas.
Conversely, if the angulation is too flat, the beam will strike the teeth at an oblique angle, causing distortion and elongation of the interproximal surfaces.
To achieve proper horizontal angulation, it is recommended to use paralleling devices, such as the Rinn XCP or the Bite-Rite. These devices ensure that the X-ray beam is directed perpendicular to the occlusal plane, providing a consistent and accurate representation of the interproximal surfaces.
Vertical Angulation
Vertical angulation refers to the angle at which the X-ray beam is directed towards the teeth from a vertical plane. Proper vertical angulation is crucial for obtaining clear and undistorted images of both the coronal and interproximal surfaces. If the vertical angulation is too high, the beam will strike the teeth from an acute angle, resulting in superimposition of the coronal and interproximal structures.
Conversely, if the vertical angulation is too low, the beam will strike the teeth from an obtuse angle, causing truncation of the coronal structures.
To achieve proper vertical angulation, the bisecting angle technique is commonly used. In this technique, the X-ray beam is directed at a 45-degree angle to the occlusal plane, dividing the angle between the long axis of the tooth and the occlusal plane.
This ensures that both the coronal and interproximal surfaces are visualized clearly and without distortion.
Tube Position and Distance, Basic principles of the bitewing technique include the:
The optimal tube position and distance for bitewing images depend on the size of the patient’s mouth and the desired field of view. The tube should be positioned centrally over the area of interest, with the distance from the tube to the film packet ranging from 10 to 15 inches.
This distance ensures that the X-ray beam covers the entire area of interest and provides sharp and focused images.
For patients with smaller mouths, a shorter tube distance may be necessary to avoid excessive distortion. Conversely, for patients with larger mouths, a longer tube distance may be required to ensure adequate coverage of the desired field of view.
Patient Positioning
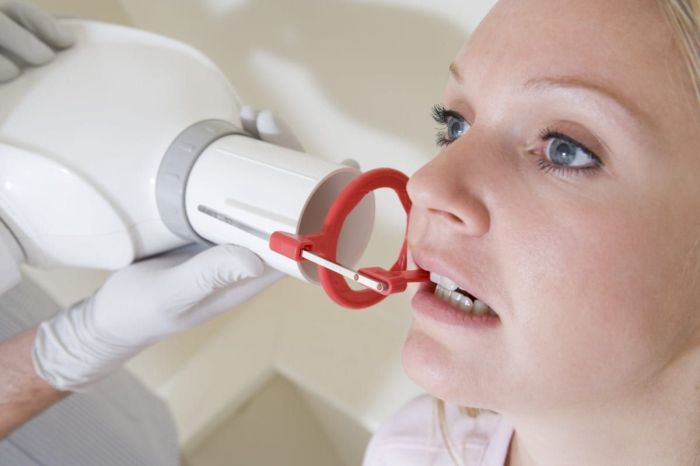
Proper patient positioning is essential for obtaining high-quality bitewing images. The patient’s head should be stabilized and maintained in a natural bite position. The Frankfort horizontal plane should be parallel to the floor, and the patient’s lips should be parted slightly to prevent interference with the film packet.
To ensure proper patient positioning, bite blocks or other devices may be used to stabilize the patient’s head and maintain a natural bite. These devices help prevent movement during exposure, which can result in blurred or distorted images.
Film Placement
Correct placement of the film packet is crucial for obtaining optimal bitewing images. The film packet should be placed between the teeth in the interproximal space, with the long axis of the film packet parallel to the long axis of the teeth.
The film packet should be positioned so that the edges of the film are not visible in the final image.
To ensure proper film placement, bite tabs or other devices may be used to stabilize the film packet. These devices help prevent movement during exposure and ensure that the film packet is positioned correctly for optimal visualization of the interproximal surfaces.
Exposure Parameters
The optimal exposure parameters for bitewing radiography include kVp, mAs, and exposure time. The kVp should be adjusted based on the patient’s size and the thickness of the bone. A higher kVp may be necessary for larger patients or for patients with thicker bone, while a lower kVp may be used for smaller patients or for patients with thinner bone.
The mAs and exposure time should be adjusted to ensure proper penetration and contrast. A higher mAs or exposure time will result in increased penetration, while a lower mAs or exposure time will result in reduced penetration. The optimal exposure parameters should be determined based on the patient’s individual needs.
Image Evaluation
Evaluation of bitewing images is essential to ensure that they are of diagnostic quality. The images should be assessed for sharpness, contrast, and distortion. Sharp images provide clear visualization of the interproximal surfaces, while adequate contrast allows for the differentiation between different structures.
Distortion can occur due to incorrect angulation, tube position, or patient movement. Common errors in bitewing radiography include superimposition, truncation, and elongation of structures. These errors can be corrected by adjusting the angulation, tube position, or patient positioning, as necessary.
FAQ: Basic Principles Of The Bitewing Technique Include The:
What is the purpose of horizontal angulation in the bitewing technique?
Horizontal angulation aims to align the X-ray beam parallel to the long axis of the teeth, ensuring the capture of interproximal surfaces without distortion or superimposition.
How does incorrect vertical angulation affect bitewing images?
Incorrect vertical angulation can lead to superimposition or truncation of structures, compromising the diagnostic value of the image.
What factors influence the optimal tube position and distance for bitewing radiography?
The patient’s mouth size and the desired field of view are key factors that determine the optimal tube position and distance.
Why is proper patient positioning crucial in the bitewing technique?
Proper patient positioning stabilizes the head and maintains a natural bite, minimizing movement and ensuring accurate image capture.