Calculate the force of attraction between Mg2+ and O2- ions using Coulomb’s Law, a fundamental principle in electrostatics. Delve into the concepts of charge, distance, and permittivity, and explore their impact on the strength of electrostatic interactions.
By understanding the interplay between these factors, we gain insights into the forces that govern the behavior of charged particles at the atomic and molecular levels.
Coulomb’s Law and Electrostatic Force: Calculate The Force Of Attraction Between Mg2+ And O2-

Coulomb’s Law is a fundamental law in electrostatics that describes the force of attraction or repulsion between two charged particles. The force is directly proportional to the product of the charges of the particles and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
The formula for Coulomb’s Law is given by:
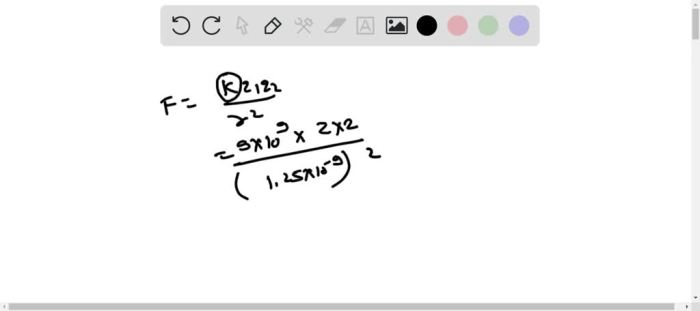
F = k – (q1 – q2) / r^2
where:
- F is the electrostatic force (in newtons)
- k is Coulomb’s constant (8.98755 × 10^9 N m^2/C^2)
- q1 and q2 are the charges of the particles (in coulombs)
- r is the distance between the particles (in meters)
Charges of Mg2+ and O2- Ions
Magnesium (Mg) has an atomic number of 12, meaning it has 12 protons and 12 electrons in its neutral state. When Mg loses two electrons, it becomes a magnesium ion (Mg2+) with a charge of +2e. Oxygen (O) has an atomic number of 8, meaning it has 8 protons and 8 electrons in its neutral state.
When O gains two electrons, it becomes an oxide ion (O2-) with a charge of -2e.
Calculating the Distance between Ions
The distance between Mg2+ and O2- ions in an ionic compound can be determined using crystallographic data or experimental techniques such as X-ray diffraction or neutron scattering. These techniques provide information about the arrangement and spacing of atoms and ions within a crystal lattice.
Permittivity and its Role, Calculate the force of attraction between mg2+ and o2-
Permittivity is a measure of the ability of a material to store electrical energy. It is defined as the ratio of the electric field strength to the electric displacement field. In vacuum, the permittivity is known as vacuum permittivity (ε0) and has a value of 8.854 × 10^-12 F/m.
The relative permittivity (εr) of a material is the ratio of the permittivity of the material to the vacuum permittivity.
Permittivity plays a crucial role in determining the strength of the electrostatic force between charged particles. A higher permittivity reduces the force, while a lower permittivity increases the force.
Numerical Calculation
To calculate the force of attraction between Mg2+ and O2- ions using Coulomb’s Law, follow these steps:
- Determine the charges of the ions: Mg2+ has a charge of +2e and O2- has a charge of
2e.
- Measure the distance between the ions: Assume the distance between the ions is 0.2 nm.
- Substitute the values into Coulomb’s Law formula: F = (8.98755 × 10^9 N m^2/C^2)
- (+2e)
- (-2e) / (0.2 nm)^2.
- Calculate the force: F =
7.19 × 10^-19 N.
The negative sign indicates that the force is attractive.
Factors Affecting the Force of Attraction
The force of attraction between Mg2+ and O2- ions can be affected by several factors:
- Charge:The greater the charges of the ions, the stronger the force of attraction.
- Distance:The farther apart the ions are, the weaker the force of attraction.
- Permittivity:The higher the permittivity of the surrounding medium, the weaker the force of attraction.
FAQ Insights
What is the significance of Coulomb’s Law?
Coulomb’s Law is a fundamental law in electrostatics that quantifies the force of attraction or repulsion between charged particles. It provides a mathematical framework for understanding and predicting the behavior of charged particles in various systems.
How does the distance between ions affect the force of attraction?
According to Coulomb’s Law, the force of attraction between ions is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. As the distance increases, the force of attraction decreases rapidly.
What role does permittivity play in electrostatic interactions?
Permittivity is a material property that represents the ability of a medium to reduce the strength of the electrostatic force between charges. It affects the magnitude of the force and can vary depending on the nature of the medium.