A farmer needs to fence a rectangular plot of land – In the realm of agriculture, fencing plays a pivotal role in defining boundaries, protecting livestock, and optimizing land utilization. For farmers tasked with enclosing a rectangular plot of land, meticulous planning and execution are paramount. This comprehensive guide will delve into the essential aspects of fencing a rectangular plot, empowering farmers with the knowledge and techniques to establish effective and durable perimeters.
As we embark on this exploration, we will examine the intricacies of perimeter calculation, explore the diverse range of fencing materials, and delve into the nuances of fence design. Furthermore, we will provide practical guidance on installation considerations, maintenance strategies, and common repair techniques.
By equipping farmers with a thorough understanding of these elements, we aim to empower them to safeguard their land and livestock while maximizing agricultural productivity.
Land Perimeter
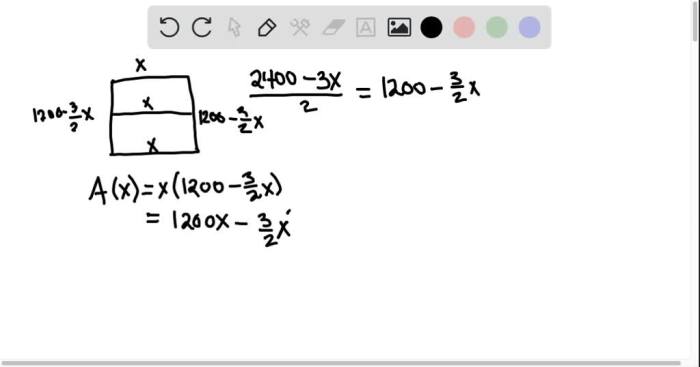
The perimeter of a rectangle is the total length of its sides. To calculate the perimeter, use the formula: Perimeter = 2(Length + Width).
For example, if a rectangular plot of land has a length of 100 feet and a width of 50 feet, the perimeter would be: Perimeter = 2(100 ft + 50 ft) = 300 feet.
Fencing Materials: A Farmer Needs To Fence A Rectangular Plot Of Land

Types of Fencing Materials
- Barbed Wire:Inexpensive and effective for containing livestock, but can be hazardous to animals and humans.
- Woven Wire:More expensive than barbed wire, but provides better protection and visibility.
- Electric Fencing:Uses an electric current to deter animals from crossing the fence, but requires a power source.
- Wood Fencing:Traditional and aesthetically pleasing, but requires regular maintenance.
- Plastic Fencing:Lightweight and durable, but can be more expensive than other materials.
Advantages and Disadvantages
- Barbed Wire:Low cost, easy to install, effective deterrent.
- Woven Wire:Better containment, visibility, durability.
- Electric Fencing:Effective deterrent, no physical barrier.
- Wood Fencing:Aesthetic appeal, natural material.
- Plastic Fencing:Lightweight, durable, low maintenance.
Fencing Design
Importance of Proper Design
Proper fencing design is crucial for agricultural purposes, ensuring effective containment, predator protection, and livestock management.
Fence Height and Spacing, A farmer needs to fence a rectangular plot of land
Fence height and spacing should be determined based on the type of livestock and the desired level of containment. For example, cattle require a higher fence (4-6 feet) with wider spacing (8-12 inches), while sheep need a lower fence (3-4 feet) with narrower spacing (4-6 inches).
Impact on Containment and Protection
The height and spacing of the fence directly impact its effectiveness in containing livestock and protecting against predators. A well-designed fence will prevent animals from escaping or being injured by predators.
Installation Considerations
Steps Involved in Installation
- Measure and Mark:Determine the perimeter of the plot and mark the corners and fence line.
- Set Posts:Install fence posts at regular intervals, ensuring they are deep enough and properly spaced.
- Attach Fencing:Stretch the fencing material between the posts, securing it with wire, staples, or other fasteners.
- Tension and Durability:Ensure the fence is properly tensioned to prevent sagging and maintain its integrity over time.
Maintenance and Repair
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular fence maintenance is essential to ensure its effectiveness and longevity. It helps prevent damage, identify problems early, and extend the fence’s lifespan.
Inspection, Cleaning, and Repair
- Inspect:Regularly check the fence for damage, loose posts, or sagging wires.
- Clean:Remove vegetation and debris that can weaken the fence or provide hiding places for pests.
- Repair:Address any damage promptly by repairing or replacing damaged sections.
Preventing Common Fence Problems
- Rust:Use galvanized or coated materials to prevent rust.
- Sagging:Ensure proper tension and support to prevent sagging.
- Animal Damage:Use appropriate fencing materials and spacing to prevent animals from damaging the fence.
Common Queries
What is the formula for calculating the perimeter of a rectangle?
Perimeter = 2(Length + Width)
What are the different types of fencing materials available?
Wood, wire, vinyl, chain-link, and electric fencing
What are the advantages of using wood fencing?
Durability, natural aesthetic, and ease of installation
What are the disadvantages of using wire fencing?
Susceptibility to rust, requires regular maintenance, and can be less aesthetically pleasing
How often should I inspect my fence for maintenance?
At least once a year, or more frequently if the fence is exposed to harsh weather conditions