Embark on a scientific journey with the student exploration triple beam balance, an essential tool for precise and accurate measurements. This guide will delve into the intricacies of this versatile instrument, empowering you with the knowledge and skills to unlock the secrets of weighing objects with confidence.
From understanding its components to mastering its techniques, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the expertise to harness the full potential of the triple beam balance in various scientific and everyday applications.
Student Exploration Triple Beam Balance: An Overview
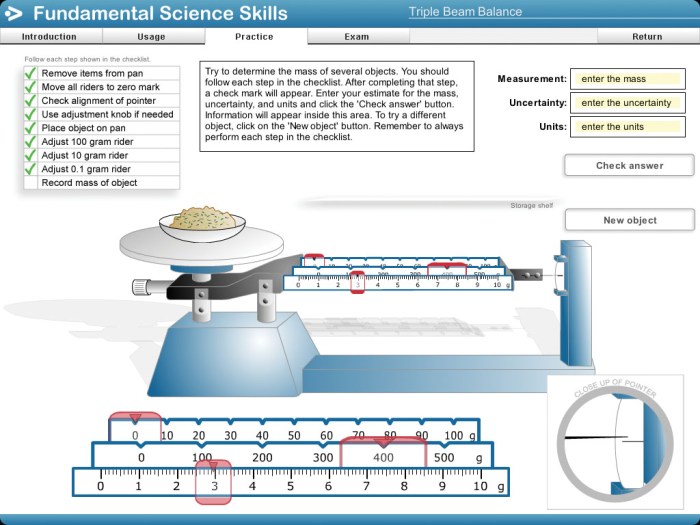
A triple beam balance is a precise instrument used to measure the mass of objects. It consists of three beams, each with a different weight capacity. The beams are calibrated to read in grams, and the total weight of the object is determined by adding the readings from each beam.
Triple beam balances are used in a variety of settings, including science labs, industrial settings, and everyday life. They are accurate and reliable, and they can be used to measure a wide range of objects.
Importance of Accuracy and Precision in Weighing Objects
Accuracy refers to the closeness of a measurement to the true value, while precision refers to the consistency of measurements. Both accuracy and precision are important when weighing objects, as they ensure that the results are reliable and reproducible.
There are a number of factors that can affect the accuracy and precision of a triple beam balance, including the calibration of the balance, the environment in which it is used, and the technique of the person using it.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Use a Triple Beam Balance
To use a triple beam balance, follow these steps:
- Place the object to be weighed on the pan.
- Move the largest beam until the pointer is at zero.
- Move the middle beam until the pointer is at zero.
- Move the smallest beam until the pointer is at zero.
- Read the weight from the beams.
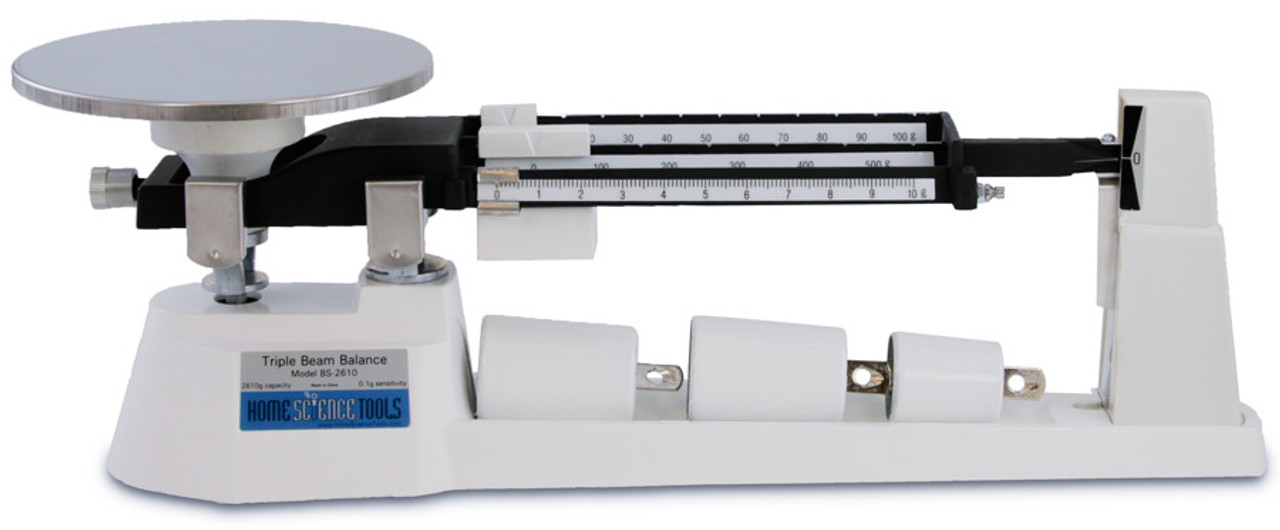
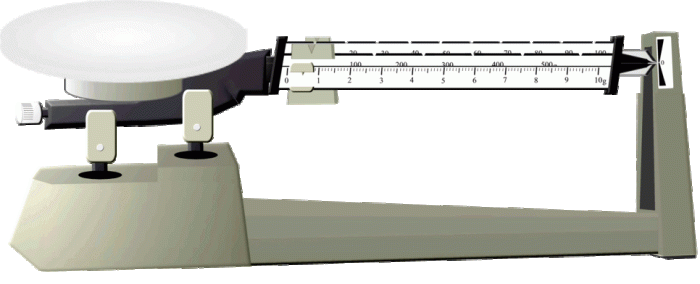
Components and Features of a Triple Beam Balance
Components of a Triple Beam Balance
- Pan: The pan is the platform on which the object to be weighed is placed.
- Beams: The beams are the three arms of the balance that are used to measure the weight of the object.
- Pointer: The pointer is a needle that indicates the weight of the object.
- Fulcrum: The fulcrum is the point on which the beams pivot.
- Base: The base is the support for the balance.
Features of a Triple Beam Balance
- Accuracy: Triple beam balances are accurate to within 0.1 grams.
- Precision: Triple beam balances are precise to within 0.01 grams.
- Durability: Triple beam balances are made of durable materials that can withstand repeated use.
- Portability: Triple beam balances are portable and can be easily transported.
- Ease of use: Triple beam balances are easy to use and can be operated by people with minimal training.
Practical Applications of a Triple Beam Balance

Science Experiments
Triple beam balances are used in a variety of science experiments, including:
- Measuring the mass of reactants and products in chemical reactions.
- Measuring the density of objects.
- Measuring the weight of objects in motion.
Industrial Settings
Triple beam balances are used in a variety of industrial settings, including:
- Measuring the weight of raw materials.
- Measuring the weight of finished products.
- Measuring the weight of objects in transit.
Everyday Life
Triple beam balances are also used in everyday life, including:
- Measuring the weight of food.
- Measuring the weight of luggage.
- Measuring the weight of mail.
Techniques for Accurate Weighing: Student Exploration Triple Beam Balance

Calibration
Triple beam balances should be calibrated before each use. To calibrate a triple beam balance, follow these steps:
- Place a known weight on the pan.
- Adjust the beams until the pointer is at zero.
- Remove the known weight.
- The balance is now calibrated.
Maintenance
Triple beam balances should be maintained regularly to ensure their accuracy and precision. To maintain a triple beam balance, follow these steps:
- Clean the balance regularly with a soft cloth.
- Lubricate the moving parts of the balance with a light oil.
- Store the balance in a dry, dust-free environment.
Tips and Best Practices
- Always use a triple beam balance on a level surface.
- Do not overload the balance.
- Do not place objects directly on the pan.
- Read the weight from the beams carefully.
- Record the weight accurately.
Troubleshooting and Error Analysis
Common Errors
- The balance is not calibrated.
- The balance is overloaded.
- The object is not placed directly on the pan.
- The beams are not moved smoothly.
- The pointer is not read correctly.
Causes of Errors
- The balance has not been calibrated recently.
- The object is too heavy for the balance.
- The object is placed on the edge of the pan.
- The beams are moved too quickly or too slowly.
- The pointer is not aligned with the zero mark.
Solutions and Strategies, Student exploration triple beam balance
- Calibrate the balance before each use.
- Use a balance that is appropriate for the weight of the object.
- Place the object directly on the center of the pan.
- Move the beams smoothly and slowly.
- Align the pointer with the zero mark before reading the weight.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the primary function of a triple beam balance?
A triple beam balance is specifically designed to measure the mass of objects with high accuracy and precision.
How do I ensure accurate measurements using a triple beam balance?
To obtain accurate measurements, ensure the balance is calibrated, use the correct beam and rider positions, and read the scale carefully.
What are some common errors that can occur when using a triple beam balance?
Common errors include parallax errors, incorrect beam and rider placement, and environmental factors affecting the balance.